

However, the most common natural barrier to entry is when the production of a product exhibits large economies of scale.
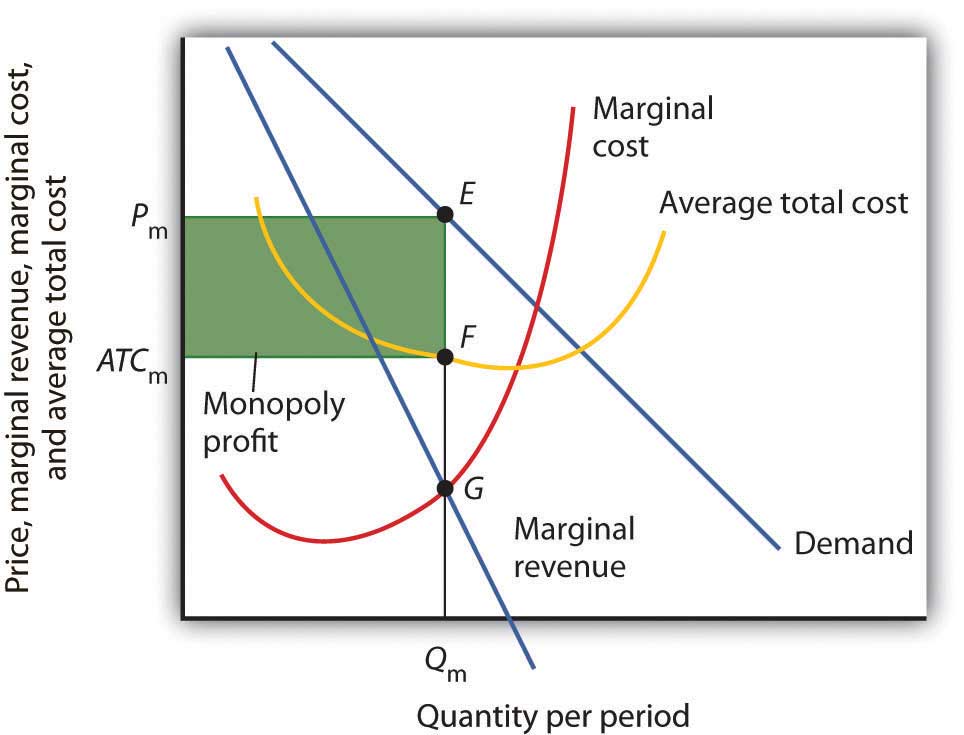
Natural barriers to entry arise from the nature of the enterprise, the quality of its workforce, or its position in the industry, rather than from legal barriers. When there are few or no barriers to entry, then either monopolistic competition results, if the product can be differentiated to some degree from close substitutes, or pure competition results when there is no significant difference among the products sold by many suppliers, which is the case for most commodities.īarriers to entry can be either natural or artificial. When barriers are not so steep, then an oligopoly results. A monopoly is created when the barriers are steep. Barriers to Entryīarriers to entry are obstacles that prevent firms from entering a market. They generally use public relations and advertising to increase awareness of their products and to maintain a good relationship with their buyers. These 3 characteristics must all be present for a monopoly to exist otherwise, a monopoly would be reduced to an oligopoly, a monopolistic competition, or even pure competition.Īnother characteristic of monopolies is that they do not need to advertise their product to increase market share. There must be significant barriers to entry so that no competitors can enter the market.
#Natural monopoly economics definition software#
For instance, there are several computer operating systems available that consumers can use, but because many people have already made significant investments in hardware and software that require specific operating systems, they cannot easily switch - they are locked into their choices.

There must be no close substitutes for the product or there must be some other economic barrier that prevents users from using substitutes.It must be a single seller in the market.To achieve this so-called market power, a monopoly must have several characteristics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
